Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker. It supports various data structures and offers extensive customizations. In this article, we’re going to discuss how you can use it to optimize a WordPress website.
WordPress Cache and Redis
WordPress caches internal application objects, like breadcrumbs, menu items, and so on, in the MySQL database. It may be quite taxing since that database also handles queries for page requests. Both combined may increase website load-times.
Redis offers a caching mechanism that substitutes MySQL database. When a user visits a WordPress website, the MySQL queries necessary to generate the page come via Redis, which also caches the results. This helps to reduce loading time.
How Does WordPress and Redis Work Together?
When a user requests a WordPress page for the first time, MySQL queries are performed on the server. Redis caches the result of those queries and stores it. So, when another user requests the same page, Redis provides the information, bypassing the database.
If the query is not cached by Redis, MySQL provides the results and then adds them to Redis cache. When a particular value is updated in the database, the corresponding Redis value becomes invalid. Therefore, you avoid serving bad cache data to the user.
Running Redis with a Docker Container
To simplify the Redis installation, we’re running it in a Docker container. To install one via Plesk, go to Server Management > Docker and search for the image, then click Run (local):
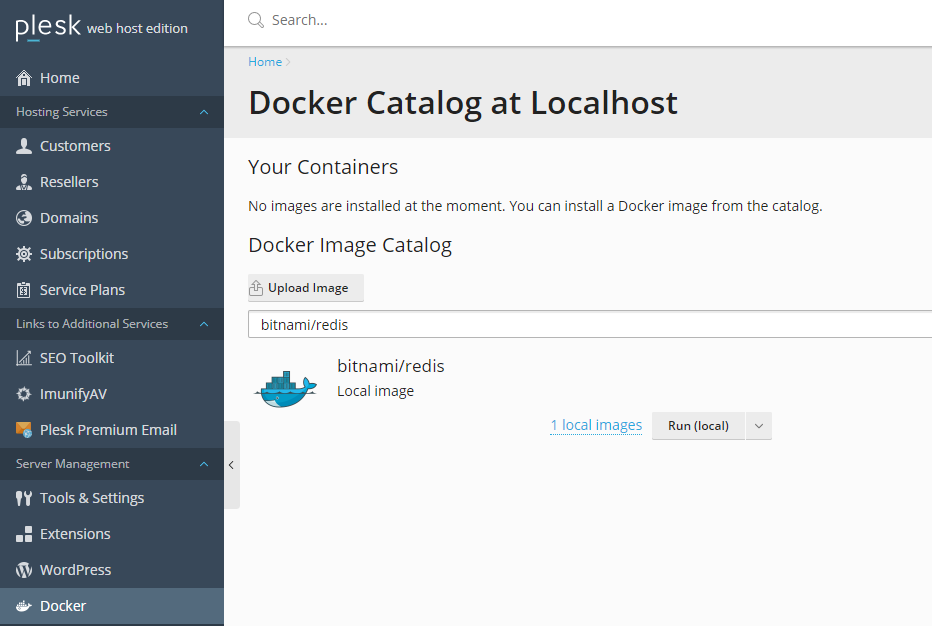
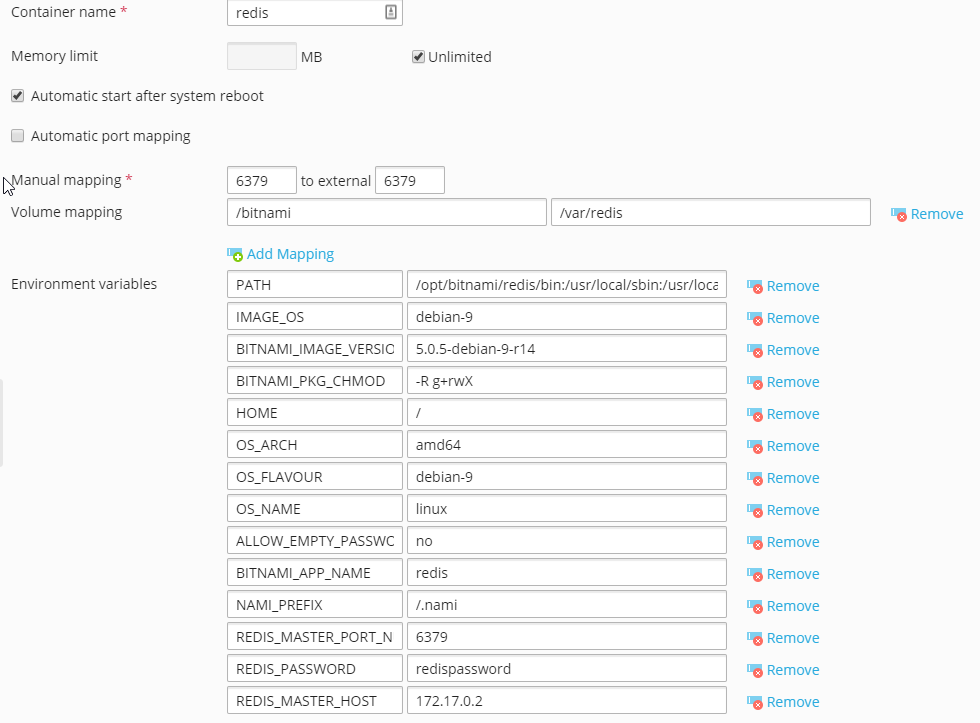
We’re using the bitnami/redis image, and the following settings (change redispassword to something else, and the IP address to IP of the container):
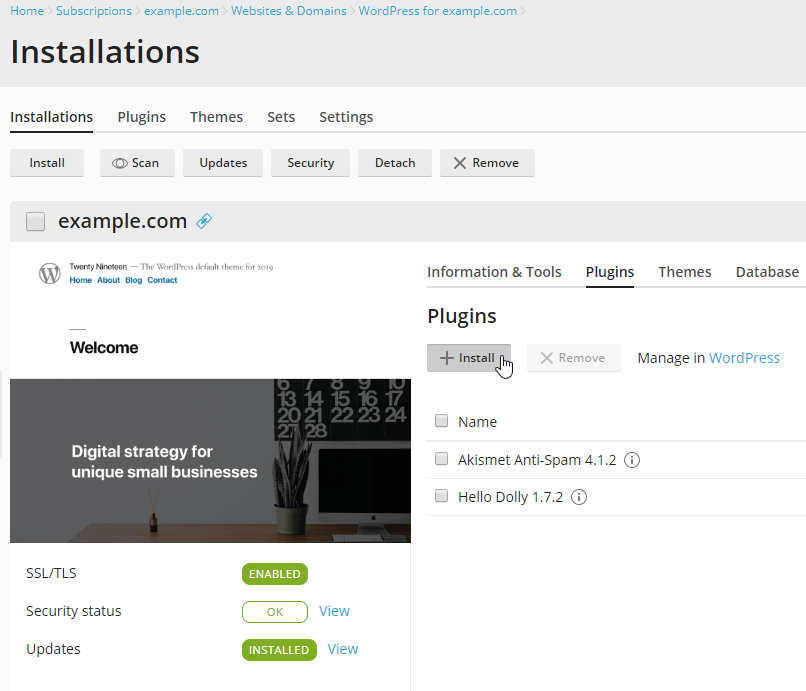
Install Redis Object Cache Plugin Via WP Toolkit
Now that our Redis server is running properly, we can install WordPress plugin Redis Object Cache to our WordPress instance using Plesk WP Toolkit:
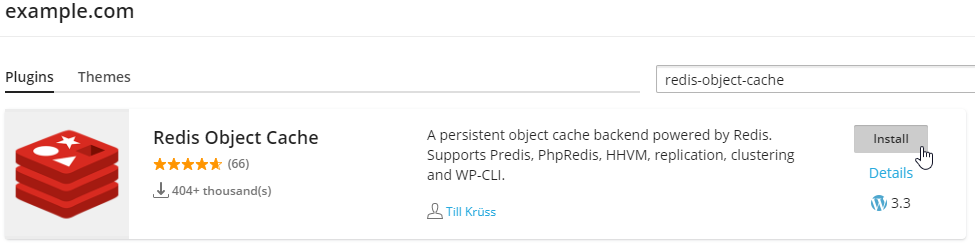
Just search the plugin name and install:
Before enabling object-cache in WordPress, you have to add the following lines in your wp-config.php file. You can do that in Plesk via File Manager.
define( 'WP_CACHE_KEY_SALT', 'example.com:' );
define( 'WP_REDIS_PASSWORD', 'redispassword' );
The first one adds a prefix to all cache keys stored in Redis. Thus, allowing you to use object-cache for multiple WordPress instances on the same server. The second protects Redis with a previously specified password.
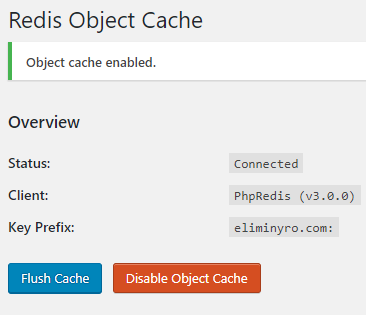
Then, you can enable object-cache in the plugin settings page – in WordPress. The final result will look something like the above screenshot.
Let us know if this guide was helpful to you and any feedback you may have on the topic!








16 Comments
HI
I have tried to follow this guide.
Firstly when I create the container in Plesk (obsidian RC3) there is more options shown such s master_password aswell as the redis password.
If i create it with config to match your example when I try to start the container it says
Error: {“message”:”cgroups: cannot find cgroup mount destination: unknown”}
OS: CloudLinux 7
Hey Chris, sorry you’ve run into some issues there. Obsidian is not a stable release yet however and we are offering additional support. Have you tried contacting one of our guys? https://support.plesk.com/hc/en-us
Additionally, as far as I know, Docker in Plesk is not very compatible with CloudLinux in general. You can either use Docker on CloudLinux manually, or host Redis container on a different platform (CentOS, Ubuntu).
Very nice post “Paul”. You have mentioned every little detail about WordPress properly. It’s areally a complete guide for a WordPress developer. Keep Posting!!
Hello, I have configured everything as you mark, but I can’t make it work.
The plugin returns “Redis server went away”
I use centos 7
Hey Gustavo,
Seems it’s best if raise a ticket with our support: https://support.plesk.com/hc/en-us
Thanks for getting in touch!
I have this same issue. “Redis server went away”. These instructions use to work for all of my sites. Now it does not work.
Hi,
I’m a Newbie to PLESK and setting up Redis Cache but I want to learn. 🙂
I’ve got several questions:
—
//1. In the Screenshot there is the value “REDIS_MASTER_PORT_N” but it seems to be cut of.
I set mine just to “REDIS_MASTER_PORT” – is this correct?
//2. I want to run Redis on my vServer – so I set “REDIS_MASTER_HOST” to the value localhost – is this correct or should I use 127.0.0.2?
//3. So I installed it on localhost to test it but it gave me an
# WARNING: The TCP backlog setting of 511 cannot be enforced because /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn is set to the lower value of 128.
How to solve this?
I’m running Plesk Obsidian 18.0.20 and Redis 5.0.6 64 bit
Hi
how can i change memory limit? for more performance. Thx
Hi, Can you specify which memory limit you’re referring to so that we can better answer your question? Thanks! 🙂
Hi,
regarding this guide I found it very useful as I was trying to do the same but I’ve faced many issues.
1. If you’re already running a redis-server in the server then the port cannot be the same for internal / external because docker cannot bind to it.
2. Redis is very lightweight but how much memory is recommended for the docker instance? 1G? 512MB? 2G? With 512MB and 2 users online it uses about 7% of memory in my simple test.
3. There seems to be a huge bottleneck when using docker instead of the local redis-server. When using local instance the site loads cached pages almost instantaneously but with redis on docker the benefits are really small. Perhaps we’re missing some extra configuration? I’ve read on bitnami issues that docker NAT is causing the bottleneck. Is it just unusuable with docker? Should we just create multiple instances on the local server instead?
Any hint would help a lot.
Installed on Centos 7. No performance increase detected. Redis requires a lot of tuning. So, it is not a plug-and-play solution, at least for wordpress. I would start with switching from centos to ubuntu. Might be a good performance tuning start
I am getting this erros:
WARNING Memory overcommit must be enabled! Without it, a background save or replication may fail under low memory condition. Being disabled, it can can also cause failures without low memory condition, see https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc/issues/1328. To fix this issue add ‘vm.overcommit_memory = 1’ to /etc/sysctl.conf and then reboot or run the command ‘sysctl vm.overcommit_memory=1’ for this to take effect.
Also memory use stay the maximum 14Mb of 4Gb
Hi Rafael,
We kindly suggest you open a ticket with our dedicated support, as they can have a look at your specific situation/errors. That said, it seems not to be Plesk related, perhaps the OS community can help you further as well.
Have followed the article. While installing Redis the default environment variables are not loading. Also the custom port mapping fields are not appearing(https://prnt.sc/fkwc7mbGq5aF). What might be the issue?? tried removing and adding the bitnami/redis container multiple times but same issue.
Hi there,
We kindly suggest you submit a request with our dedicated support, as they can have a closer look at your specific setup. Hope this helps!